How To Treat Gum Infections
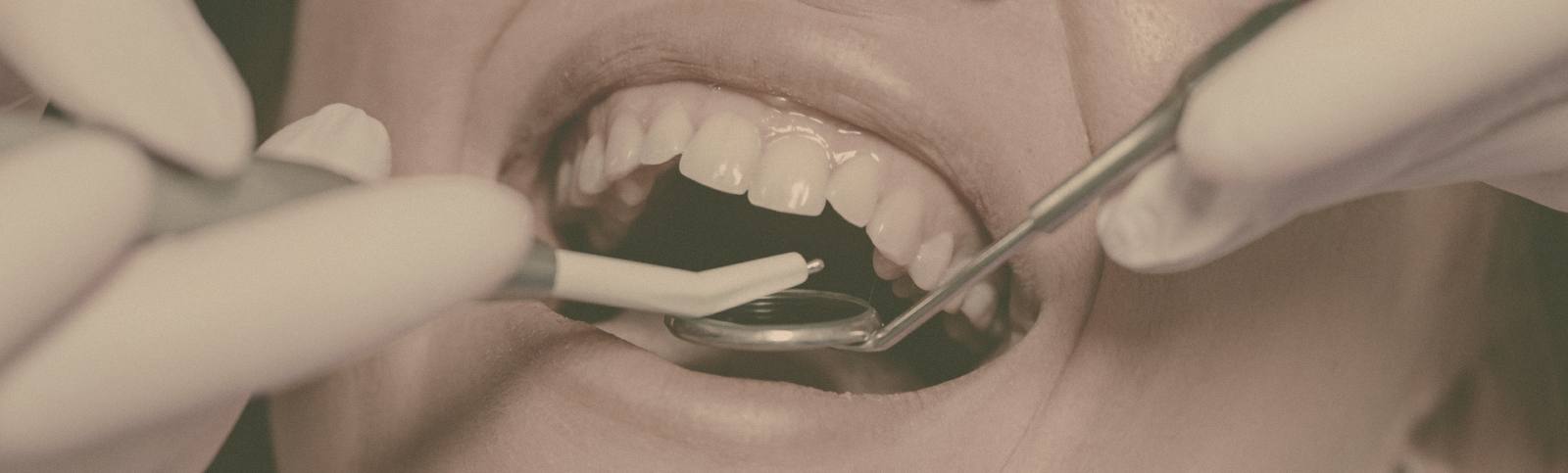 Infected gum treatment involves using an antibiotic to kill off the bacteria causing the infection. Antibiotics, like metronidazole (Flagyl), are effective in preventing and controlling bacterial growth. They work by preventing the bacteria from forming walls and reproducing. The following are some of the most common antibiotics used for gum disease. Infected gum treatment may also involve the removal of a tooth.
Infected gum treatment involves using an antibiotic to kill off the bacteria causing the infection. Antibiotics, like metronidazole (Flagyl), are effective in preventing and controlling bacterial growth. They work by preventing the bacteria from forming walls and reproducing. The following are some of the most common antibiotics used for gum disease. Infected gum treatment may also involve the removal of a tooth.Infections of the gum tissue can lead to an abscess, a pocket of pus in the mouth. If left untreated, this infection can become worse and cause pain. The tissue infected can even spread to the jaw bone, putting the tooth's root at risk. During the course of this process, the bacteria can enter the bloodstream and cause major problems. Therefore, infected gum treatment is essential.
A more invasive form of gum treatment is known as a gingivectomy. This procedure involves lifting the gums back and removing any tartar that's causing infection. If the disease has spread to the bone that supports the tooth, a gingivectomy is performed to remove the affected tissue. This surgery is reserved for severe cases and aims to stop the progression of the disease. A flap surgery, on the other hand, aims to replace the bone surrounding the tooth.
If the gum treatment fails, a warm cup of water and hydrogen peroxide mouthwash are two simple home remedies for inflamed gum. The hydrogen peroxide in these mouthwashes is a great natural antibacterial and antifungal agent, which can kill germs and treat many oral issues. To use the mouthwash, you should mix three per cent hydrogen peroxide solution with water and gargle it for about 20 seconds.
Turmeric is another home remedy for gum infections. This powder contains antibacterial and antifungal properties. Apply the paste to your gums twice daily and rinse with warm water. A simple antibacterial paste made of almond oil or coconut oil can also be applied to the gums. Alternatively, aloe vera mouthwash is a natural antibiotic with similar properties to the antiseptic chlorhexidine found in store-bought mouthwash. Apply this paste twice a day to prevent inflammation.
While a dentist may be able to treat your infection effectively and safely, it can cause further damage to your teeth and your body. Periodontitis, an infection of the gums, is a serious condition that requires emergency dental service. In addition to the discomfort associated with gum disease, periodontitis can affect your bones and immune system. As a result, the treatment for this condition is essential to keep your teeth healthy.
Types of Gum Infection
There are 3 main types of gum disease. The first is gingivitis, the second is periodontitis and the third is laryngitis. Prevention is crucial, but treatment is key if it is caught in its early stages. Typically, gum disease is caused by a buildup of plaque, a sticky substance that contains bacteria. When plaque builds up on the teeth, the immune system tries to eliminate the bacteria by inflaming the gum around the tooth. This causes redness and swelling.
Gingivitis Gum Infection
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that can be caused by a number of factors, including tooth decay, poor oral hygiene, and viral infections. Gingivitis is characterized by redness, swelling, and a loss of tooth tissue. It can lead to the development of periodontitis, an infection that affects the tooth support structures (gums, bones, and ligaments) around your teeth. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to serious health problems such as decreased bone density and loss of teeth.
Periodontitis Gum Infection
Periodontitis is an infection that affects the tooth support structures (gums, bones, and ligaments) around your teeth. Periodontitis is typically caused by bacteria that have entered the gum tissue from the mouth environment. This type of gum infection is often referred to as advanced gingivitis.
Laryngitis Gum Infection
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the voice box (larynx). It can be caused by a number of factors, including viral infections, allergies, or environmental exposure to toxins (such as smoke). Laryngitis is characterized by hoarseness (a change in the sound of your voice) and difficulty speaking.
Article kindly provided by emergencydentistcheadle.co.uk
Latest Articles
- How Oral Health Quietly Influences Energy Sleep and Long Term Well Being
- How Emotions Affect Your Skin
- Everyday Walks as Brain Games for Your Dog
- How Light Weights Can Build Serious Strength
- Missing Dental Supplies and What They're Really Telling You
- Rethinking Early Intervention Strategies for Childhood Behavior Support
- Keep Going: The Brain Science of Turning Setbacks Into Momentum
- Designing Movement Routines That Don't Feel Like Exercise
- Chair Yoga Works Wonders For Bodies Of All Ages
- Eyebrows Through the Ages and What They Reveal About Our Faces
- Feeding Plans That Keep Every Pet in Balance
- Hidden Immune Boost Hiding in Plain Sight for Corporate Travellers
- Evening Quiet Isn't Automatic and That's Perfectly Normal
- Quiet Power Makes a Salon Feel Like a VIP Retreat
- Chewing as Meditation and Everyday Calm
- Sleep Deprivation as a Social Problem, Not a Personal Failure
- Why Recovery Rituals Outlast Resolutions and Keep Us Moving Forward
- Desk Job Survival with a Side of Shoulder Rolls
- Why Your Living Room Layout Might Be Causing Your Back Pain
- Why Your Teeth Love Dental Hygienists
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Exercise and Fitness
- Meditation and Yoga
- Mental Health
- Women's Health
- Men's Health
- Children's Health
- Senior Health
- Heart Health
- Sleep Health
- Skin Health
- Eye Health
- Dental Health
- Pain Management
- Addiction and Recovery
- Sexual and Reproductive Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Chronic Conditions
- Weight Management
- Occupational Health and Safety
- Public Health
- General Health Tips
- Beauty

